StyleGAN
- Introduction
Input latent space 가 train data 의 probability 를 따르다보면, entanglement 발생
StyleGAN 에선 intermediate latent space 를 사용함으로서 disentangle 시킬 수 있음
Perceptual path length 와 Linear seperability 를 제안
- Method

기존 PGGAN 에서 z 를 input 으로 주던 것과 달리, StyleGAN 에선 Constant 로 부터 시작함
z 는 non-linear mapping network f 를 통해 w 로 mapping
Mapping network f 는 8 layer MLP 로 512 dimension 을 갖도록 구성
w 를 $\mathbf{A}$: affine transformation 을 통해 $\mathbf{y}=\left(\mathbf{y}_s, \mathbf{y}_b\right)$ 로 specialize
$\mathbf{y}$ 를 통해 Adaptive instance normalization (AdaIN) 을 조절
$\operatorname{AdaIN}\left(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{y}\right)=\mathbf{y}_{s, i} \frac{\mathbf{x}_i-\mu\left(\mathbf{x}_i\right)}{\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_i\right)}+\mathbf{y}_{b, i}$
$\mathbf{B}$: Gaussian noise inputs
Style Mixing

Two latent codes $\mathbf{z}_1, \mathbf{z}_2$ is fed to the mapping network and gives $\mathbf{w}_1, \mathbf{w}_2$ as output
Reduce the correlation between adjacent styles → 좀 더 다양한 style 의 output 이 나오도록 하는 reg 라고 생각됨
Coarse spatial resolutions ($4^2-8^2$): High-level aspects (pose, general hair style, face shape, eyeglasses)
Middle spatial resolutions ($16^2-32^2$): Smaller scale facial features, hair style, eyes open/closed
Fine spatial resolutions ($64^2-1024^2$): Color scheme, microstructure
Stochastic Variance


Noise 를 주입함으로써 머리 detail 같은게 더 살아있음
Disentanglement Studies
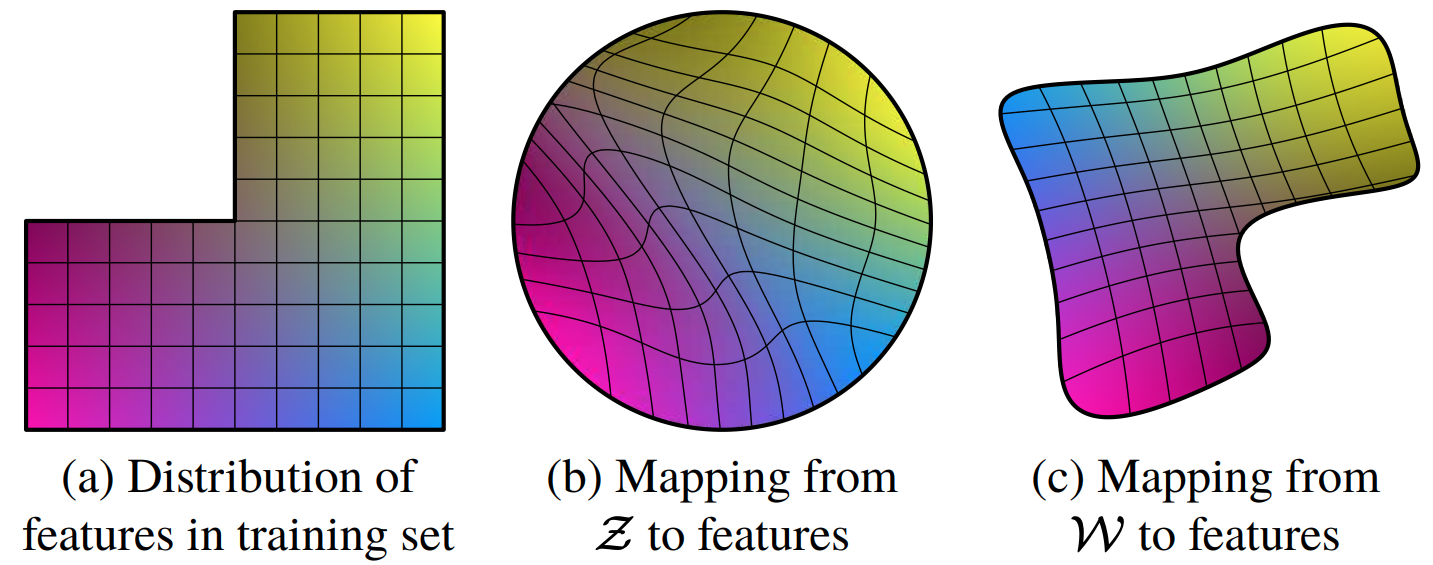

Mapping from $\mathcal{Z}$ (Gaussian) to features has restricted distribution → Entangled
Mapping from $\mathcal{W}$ to features changes distribution of features desirably → Disentangled
Perceptual Path Length
이 metric 은 latent space 에서 linear interpolation 을 진행함에 따라 image 가 얼마나 drastically 변하는지를 측정
$l_{\mathcal{Z}}=\mathbb{E}\left[\frac{1}{\epsilon^2} d\left(G\left(\operatorname{slerp}\left(\mathbf{z}_1, \mathbf{z}_2 ; t\right)\right)\right.\right.,\left.\left.G\left(\operatorname{slerp}\left(\mathbf{z}_1, \mathbf{z}_2 ; t+\epsilon\right)\right)\right)\right]$, $G=g \circ f$
$l_{\mathcal{W}}=\mathbb{E}\left[\frac{1}{\epsilon^2} d\left(g\left(\operatorname{lerp}\left(f\left(\mathbf{z}_1\right), f\left(\mathbf{z}_2\right) ; t\right)\right)\right.\right.\left.\left.g\left(\operatorname{lerp}\left(f\left(\mathbf{z}_1\right), f\left(\mathbf{z}_2\right) ; t+\epsilon\right)\right)\right)\right]$
Linear Separability
이 metric 은 linear SVM 을 통해 latent-space points 가 얼마나 잘 separate 되는지 측정
FFHQ
FlickrFaces-HQ
70000 images $1024^2$ resolution
Truncation trick in $\mathcal{W}$
Truncated 또는 Shrunk sampling space 가 image quality 를 향상시키는 경향이 있음
Center of mass of $\mathcal{W}$: $\overline{\mathbf{w}}=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{z} \sim P(\mathbf{z})}[f(\mathbf{z})]$
Scale the deviation of $\mathbf{w}$: $\mathbf{w}^{\prime}=\overline{\mathbf{w}}+\psi(\mathbf{w}-\overline{\mathbf{w}})$
- Experiment


StyleGAN2
- Introduction
Problems
- Instance normalization layer causes artifacts
- Progressive growing leads to phase artifacts: High-frequency detail is learned and fixed in the lower resolutions


New techniques
- Fixed-side step in W results in a fixed-magnitude change in the image → Smooth change
- A new inversion algorithm → Image to latent vector
- Method

Removing normalization artifacts
64*64 부터 blob-shaped artifact 등장하여 resolution 이 증가할수록 더 또렷해짐
이 문제의 원인으로 AdaIN 을 꼽음
Generator architecture revisited
기존 StyleGAN 에선 각자 다른 style 를 갖는 style block 이 존재함
이 style block 안에 noise 인 $\mathbf{B}$ 와 bias 인 $b_i$ 가 존재하는데, 현재 style 의 강도 (magnitude) 에 상대적으로 반비례하는 영향을 미침
따라서 noise 와 bias 를 style block 밖으로 옮겨 normalized data 에 작동하도록 하여 좀 더 predictable 한 결과를 얻을 수 있었음
또한 이런 변화를 주고나니 기존에 mean, std 에 modulation 과 normalization 을 실행하던게 mean 을 빼고 std 에만 적용해도 충분하다는 사실을 알게됨
Instance normalization revisited
StyleGAN 의 강점 중 하나인 style mixing 은 각 layer 에 서로 다른 latent w 를 주는 것으로 이미지를 조절
근데 이렇게 여러 layer 에 w 를 주다보니, 특정 feature map 이 강해지는 경우도 발생
Style block 을 살펴보면 다음과 같이 구성

Modulation
Incoming style 에 따라 input feature map 을 scale
$w_{i j k}^{\prime}=s_i \cdot w_{i j k}$ (weight scaling)
Normalization (Demodulation)
Normalization 의 목적은 modulation 후 convolution 을 거쳐 나온 feature map 에서 scaling 의 영향을 제거
따라서 modulation 과 convolution 을 거쳐 나온 std 가 다음과 같이 구성되어 있을 때,
$\sigma_j=\sqrt{\sum_{i, k} w_{i j k}^{\prime}}$
이것을 다시 demodulation 해주는 과정이 필요함
$w_{i j k}^{\prime \prime}=w_{i j k}^{\prime} / \sqrt{\sum_{i, k} w_{i j k}^{\prime}{ }^2+\epsilon}$
따라서 AdaIN 을 modulation - demodulation 으로 변경
Lazy regularization
다음 R1 regularizaiton 을 16 batch 마다 느리게 계산하여 computational resource 를 save
$R_1(\psi)=\frac{\gamma}{2} E_{p D(x)}\left[\left\|\nabla D_\psi(x)\right\|^2\right]$
Path length regularization
w 가 바뀌면 g(w) 도 똑같이 바뀜
$\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{w}, \mathbf{y} \sim \mathcal{N}(0, \mathbf{I})}\left(\left\|\mathbf{J}_{\mathbf{w}}^T \mathbf{y}\right\|_2-a\right)^2$
Progressive growing
Progressive growing 으로 인해 high-frequency detail 이 low resolution 에서 학습되고 고정
따라서 progressive growing 을 없애고 G 와 D 는 고정된 구조

- Experiment
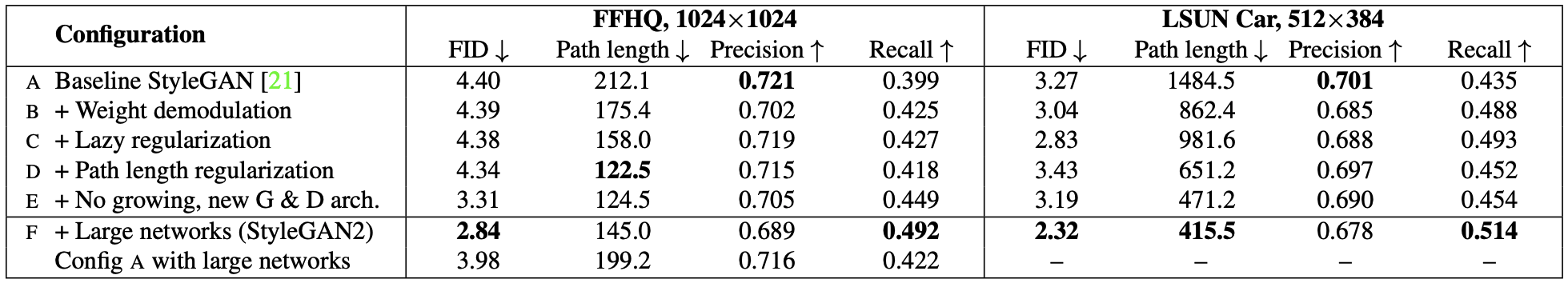
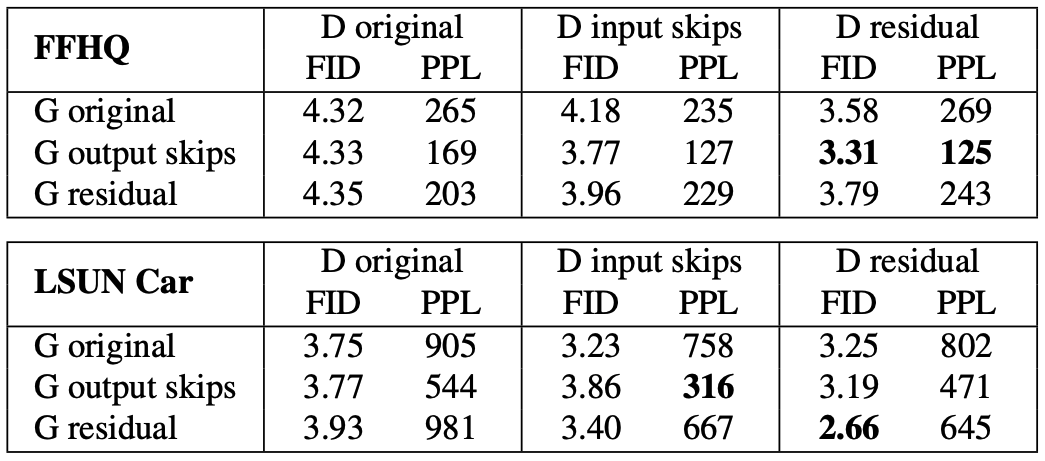
- Reference
[1] Karras, Tero et al. "A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks." CVPR 2019 [Paper link]
[2] Karras, Tero, et al. "Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan." CVPR 2020 [Paper link]